In a world striving for sustainable energy solutions, the spotlight shines brightly on solar energy and its transformation into electricity. The boundless radiance of the Sun fuels our planet with more than just natural warmth and light – it holds the key to generating clean and renewable electricity. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate workings of solar energy and its remarkable conversion into usable electricity.
Discover the marvels of photovoltaic technology as we unravel the process of how solar panels capture sunlight and translate it into a potent stream of electrical energy. From the mesmerizing photovoltaic effect to the intricate manufacturing processes behind solar panels, we demystify the science that powers this revolutionary energy source.
Explore the journey from silicon ingots to fully operational solar modules, uncovering the intricate steps that enable us to harness the Sun’s brilliance. Dive into the world of solar electricity, where photons become charged electrons, generating the power to illuminate homes, power appliances, and even feed excess energy back into the grid.
But our exploration doesn’t stop at the technical aspects. We also delve into the broader significance of solar energy and electricity. Discover how these technologies contribute to reducing carbon footprints, mitigating climate change, and paving the way towards a cleaner and greener future.
Whether you’re a renewable energy enthusiast, an environmental advocate, or simply curious about the science behind solar power, this guide is your passport to understanding the fundamental concepts that illuminate our world, both literally and figuratively. Join us on this enlightening journey through solar energy and electricity, where innovation meets sustainability in a dance of electrons and hope.
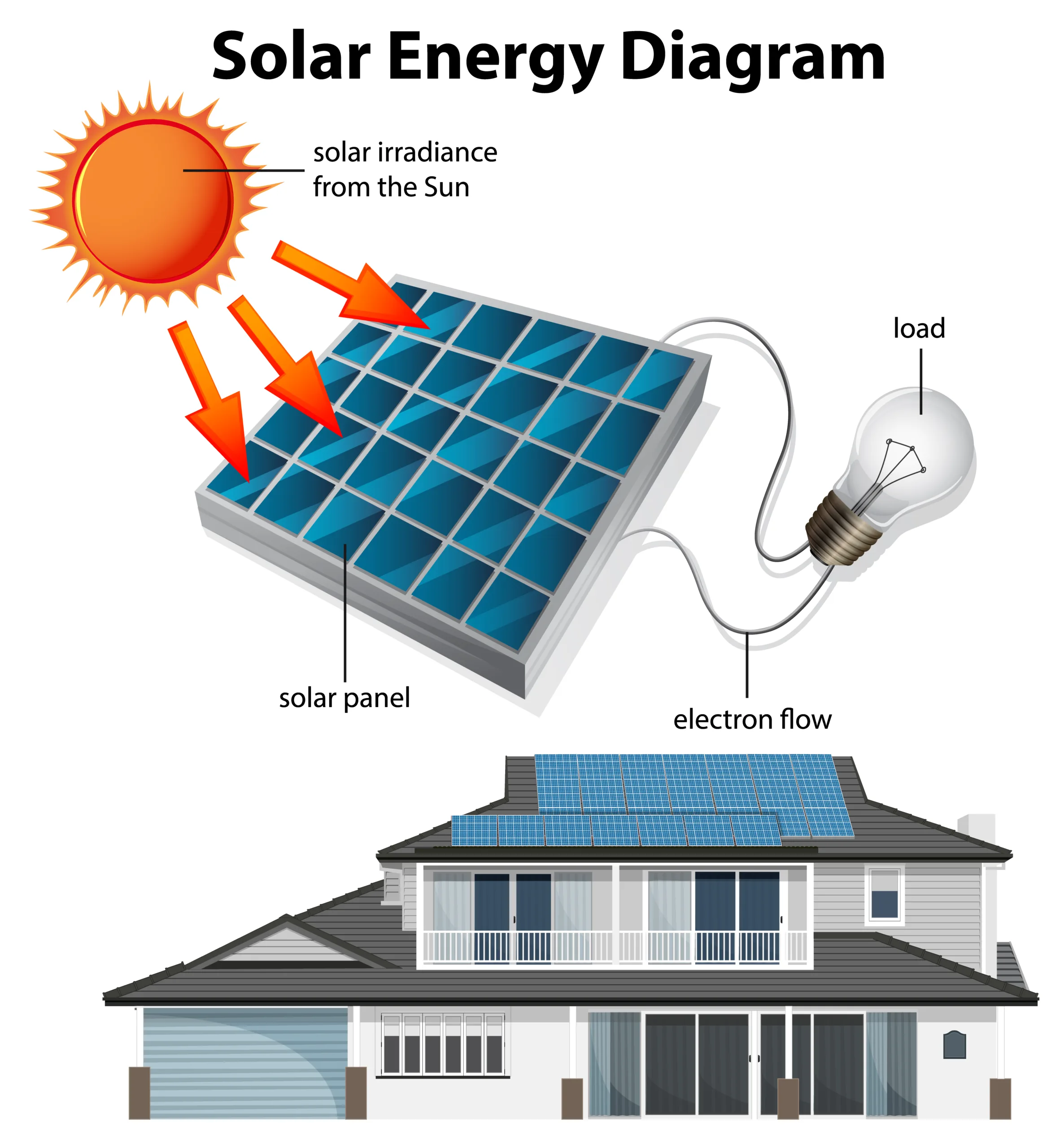
how is solar energy converted into electricity
Solar panels work by harnessing the energy from sunlight and converting it into electricity through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. Here’s a brief overview of how solar panels work and how solar electricity is produced:
- Photovoltaic Cells: Solar panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are typically made from silicon or other semiconductor materials. These cells are designed to absorb photons (particles of light) from sunlight.
- Absorption of Photons: When sunlight hits the PV cells, the photons are absorbed by the semiconductor material. This energy from the photons excites electrons within the material, causing them to become energized and break free from their usual positions in the atoms.
- Generation of Electric Current: The movement of these energized electrons creates an electric current. PV cells have an electric field that directs the movement of these electrons, causing them to flow in a specific direction.
- Electricity Production: The flow of electrons in the electric field creates a flow of electric current, and this current can be captured and harnessed as electricity. The PV cells are connected in an organized pattern to form a solar panel, and multiple panels are often connected together to create a solar array.
- Inverter Conversion: The electricity generated by the solar panels is in direct current (DC) form. However, most of our electrical appliances and systems run on alternating current (AC). To make the electricity usable, an inverter is used to convert the DC electricity from the panels into AC electricity that can be used in homes and businesses.
- Usage and Storage: The converted AC electricity can now be used to power household appliances, lights, electronics, and more. Any excess electricity generated that is not immediately used can be stored in batteries or fed back into the grid, depending on the setup and the availability of net metering programs.

How are the solar panels made
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are made using a multi-step manufacturing process that involves several layers of materials. The most common type of solar panel is based on silicon technology. Here’s an overview of how solar panels are made:
- Silicon Ingot Production:
The process begins with the production of silicon ingots. These ingots are cylindrical blocks of high-purity crystalline silicon. The silicon used in solar panels is typically derived from sand, which is purified and then melted to form ingots through a process called the Czochralski method or the Float Zone method. - Wafer Slicing:
The silicon ingots are then sliced into thin wafers using a diamond wire saw or a similar cutting method. These wafers are usually around 150-200 micrometers thick and are circular in shape. - Wafer Surface Treatment:
The sliced wafers are cleaned and treated to remove any impurities and create a smooth surface. This process involves etching and cleaning to ensure the proper adhesion of subsequent layers. - Doping and Junction Formation:
Doping involves introducing specific impurities (such as phosphorus and boron) into the surface of the silicon wafers to create a “p-n” junction, which is essential for the photovoltaic effect. This creates regions with an excess of electrons (n-type) and regions with a deficit of electrons (p-type) on the wafer. - Anti-Reflective Coating:
An anti-reflective coating is applied to the front surface of the silicon wafer to reduce the loss of sunlight due to reflection. This coating enhances the absorption of sunlight by the photovoltaic cells. - Metal Contacts:
Metal contacts, usually made of silver or another conductive material, are printed onto the front and back surfaces of the wafer. These contacts facilitate the flow of electrons within the solar cell. - Encapsulation:
The solar cell is encapsulated to protect it from environmental factors and ensure its durability. This encapsulation involves using a layer of ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) or similar material, which is then sandwiched between a layer of glass or a transparent plastic sheet and a backsheet material. - Module Assembly:
Multiple solar cells are connected together to form a solar module or panel. They are wired in series or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and current levels. These interconnected cells are laminated together with additional EVA and protective materials. - Framing and Testing:
The solar panel is placed within a frame to provide structural support and protection. Before the panels are released for use, they undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance and quality standards.
Once the solar panels are manufactured, they can be installed on rooftops, ground mounts, or integrated into various systems to generate electricity from sunlight. It’s important to note that while the process outlined above is typical for silicon-based solar panels, there are also other types of solar technologies, such as thin-film and organic solar cells, which have different manufacturing processes.
Above article is just for information and elaborate study is needed for the production of good quality solar panels for the production and harnessing energy of the Sun.


